IEEE 2014 / 2013-Image Processing Projects
IEEE 2014 TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
Abstract — Image re-ranking, as an effective way to improve the results of web-based image search, has been adopted by current commercial search engines. Given a query keyword, a pool of images is first retrieved by the search engine based on textual information. By asking the user to select a query image from the pool, the remaining images are re-ranked based on their visual similarities with the query image. A major challenge is that the similarities of visual features do not well correlate with images’ semantic meanings which interpret users’ search intention. On the other hand, learning a universal visual semantic space to characterize highly diverse images from the web is difficult and inefficient. In this paper, we propose a novel image re-ranking framework, which automatically offline learns different visual semantic spaces for different query keywords through keyword expansions. The visual features of images are projected into their related visual semantic spaces to get semantic signatures. At the online stage, images are re-ranked by comparing their semantic signatures obtained from the visual semantic space specified by the query keyword. The new approach significantly improves both the accuracy and efficiency of image re-ranking. The original visual features of thousands of dimensions can be projected to the semantic signatures as short as 25 dimensions. Experimental results show that 20% ��35% relative improvement has been achieved on re-ranking precisions compared with the state of- the-art methods.
Captcha as Graphical Passwords—A New Security Primitive Based on Hard AI Problems
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION FORENSICS AND SECURITY
Abstract—Many security primitives are based on hard mathematical problems. Using hard AI problems for security is emerging as an exciting new paradigm, but has been underexplored. In this paper, we present a new security primitive based on hard AI problems, namely, a novel family of graphical password systems built on top of Captcha technology, which we call Captcha as graphical passwords (CaRP). CaRP is both a Captcha and a graphical password scheme. CaRP addresses a number of security problems altogether, such as online guessing attacks, relay attacks, and, if combined with dual-view technologies, shoulder-surfing attacks. Notably, a CaRP password can be found only probabilistically by automatic online guessing attacks even if the password is in the search set. CaRP also offers a novel approach to address the well-known image hotspot problem in popular graphical password systems, such as PassPoints, that often leads to weak password choices. CaRP is not a panacea, but it offers reasonable security and usability and appears to fit well
Online Payment System using Steganography and Visual Cryptography
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
Abstract—A rapid growth in E-Commerce market is seen in recent time throughout the world. With ever increasing popularity of online shopping, Debit or Credit card fraud and personal information security are major concerns for customers, merchants and banks specifically in the case of CNP (Card Not Present). This paper presents a new approach for providing limited information only that is necessary for fund transfer during online shopping thereby safeguarding customer data and increasing customer confidence and preventing identity theft. The method uses combined application of steganography and visual cryptography for this purpose.
Semi-Supervised Biased Maximum Margin Analysis for Interactive Image Retrieval
IEEE 2014 TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING
Abstract— With many potential practical applications, Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) has attracted substantial attention during the past few years. A variety of Relevance Feedback (RF) schemes have been developed as a powerful tool to bridge the semantic gap between low-level visual features and high-level semantic concepts and thus to improve the performance of CBIR systems. Among various RF approaches, Support Vector Machine (SVM) based RF is one of the most popular techniques in CBIR. Despite the success, directly using SVM as a RF scheme has two main drawbacks. First, it treats the positive and negative feedbacks equally, which is not appropriate since the two groups of training feedbacks have distinct properties. Second, most of the SVM based RF techniques do not take into account the unlabelled samples although they are very helpful in constructing a good classifier. To explore solutions to overcome these two drawbacks, in this work, we propose a Biased Maximum Margin Analysis (BMMA) and a Semi-Supervised Biased Maximum Analysis (Semi BMMA), for integrating the distinct properties of feedbacks and utilizing the information of unlabeled samples for SVM based RF schemes. The BMMA differentiates positive feedbacks from negative ones based on local analysis, while the Semi BMMA can effectively integrate information of unlabelled samples by introducing a Laplacian regularize to the BMMA. We formulate the problem into a general subspace learning task and then propose an automatic approach of determining the dimensionality of the embedded subspace for RF. Extensive experiments on a large real world image database demonstrate that the proposed scheme combined with the SVM RF can significantly improve the performance of CBIR systems.
IEEE 2014 TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIA
Abstract—Forward Error Correction (FEC) is one of the most common means of performing packet error recovery in data transmissions. FEC schemes typically tune the FEC rate in accordance with feedback information provided by the receiver. However, the feedback and FEC rate calculation processes inevitably have a finite duration, and thus the FEC rate implemented at the sender may not accurately reflect the current state of the network. Thus, this paper proposes an Enhanced Random Early Detection Forward Error Correction (ERED-FEC) mechanism to improve the quality of video transmissions over Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs). In contrast to most FEC schemes, the FEC redundancy rate is calculated directly at the Access Point (AP). Moreover, the redundancy rate is tuned in accordance with both the wireless channel condition (as indicated by the number of packet retransmissions) and the network traffic load (as indicated by the AP queue length). The experimental results show that the proposed ERED-FEC mechanism achieves a significant improvement in the video quality compared to existing FEC schemes without introducing an excessive number of redundant packets into the network.
A Stochastic Approach to Image Retrieval Using Relevance Feedback and Particle Swarm Optimization
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIDEDIA
Abstract—Understanding the subjective meaning of a visual query, by converting it into numerical parameters that can be extracted and compared by a computer, is the paramount challenge in the field of intelligent image retrieval, also referred to as the ??semantic gap?? Problem. In this paper, an innovative approach is proposed that combines a relevance feedback (RF) approach with an evolutionary stochastic algorithm, called particle swarm optimizer (PSO), as a way to grasp user's semantics through optimized iterative learning. The retrieval uses human interaction to achieve a twofold goal: 1) to guide the swarm particles in the exploration of the solution space towards the cluster of relevant images; 2) to dynamically modify the feature space by appropriately weighting the descriptive features according to the users' perception of relevance. Extensive simulations showed that the proposed technique outperforms traditional deterministic RF approaches of the same class, thanks to its stochastic nature, which allows a better exploration of complex, nonlinear and highly-dimensional solution spaces.
 |
| Add caption |
A multi-resolution image fusion scheme for 2D images based on wavelet transform
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON VISUAL INFORMATION ENGINEERING
Abstract—The fusion of images is the process of combining two or more images into a single image retaining important features from each of the images. A scheme for fusion of multi-resolution 2D gray level images based on wavelet transform is presented in this paper. If the images are not already registered, a point-based registration, using affine transformation is performed prior to fusion. The images to be fused are first decomposed into sub images with different frequency and then information fusion is performed using these images under the proposed gradient and relative smoothness criterion. Finally these sub images are reconstructed into the result image with plentiful information. A quantitative measure of the degree of fusion is estimated by cross-correlation coefficient and comparison with some of the existing wavelet transform based image fusion techniques is carried out.
A Proposal to Prevent Click-Fraud Using Clickable CAPTCHAs
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON SOFTWARE SECURITY AND RELIABILITY COMPANION
Abstract—Advertising on the Internet is a key factor for the success of several businesses nowadays. The Internet has evolved to a point where it has become possible to develop a business model completely based on Web advertising, which is important for the consolidation of such a model and the continuity of the Internet itself. However, it is often observed that some content publishers are dishonest and employ automated tools to generate traffic and profit by defrauding advertisers. Similarly, some advertisers use automated tools to click on the ads of their competitors, aiming to exhaust the budget of the competitor's marketing departments. In this paper, differently of recent click fraud detection mechanisms, that take place after the fraud has already occurred, we propose an approach for preventing automated click-fraud, based on the use of click able CAPTCHAs.
Intent Search: Capturing User Intention for One-Click Internet Image Search
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON PATTERN ANALYSIS & MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
Abstract—Web-scale image search engines (e.g., Google image search, Bing image search) mostly rely on surrounding text features. It is difficult for them to interpret users' search intention only by query keywords and this leads to ambiguous and noisy search results which are far from satisfactory. It is important to use visual information in order to solve the ambiguity in text-based image retrieval. In this paper, we propose a novel Internet image search approach. It only requires the user to click on one query image with minimum effort and images from a pool retrieved by text-based search are re ranked based on both visual and textual content. Our key contribution is to capture the users' search intention from this one-click query image in four steps. 1) The query image is categorized into one of the predefined adaptive weight categories which reflect users' search intention at a coarse level. Inside each category, a specific weight schema is used to combine visual features adaptive to this kind of image to better re rank the text-based search result. 2) Based on the visual content of the query image selected by the user and through image clustering, query keywords are expanded to capture user intention. 3) Expanded keywords are used to enlarge the image pool to contain more relevant images. 4) Expanded keywords are also used to expand the query image to multiple positive visual examples from which new query specific visual and textual similarity metrics are learned to further improve content-based image re ranking. All these steps are automatic, without extra effort from the user. This is critically important for any commercial web-based image search engine, where the user interface has to be extremely simple. Besides this key contribution, a set of visual features which are both effective and efficient in Internet image search are designed. Experimental evaluation shows that our approach significantly improves the precision of top-ranked images and also the user experience.
Visual cryptography Scheme for color Image Using Random number - eStamp Authentication
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER & COMMUNICATION
Abstract— Visual Cryptography is a special encryption technique to hide information in images in such a way that it can be decrypted by the human visual system. The benefit of the visual secret sharing scheme is in its decryption process where without any complex cryptographic computation encrypted data is decrypted using Human Visual System (HVS). But the encryption technique needs cryptographic computation to divide the image into a number of parts let n. k-n secret sharing scheme is a special type of Visual Cryptographic technique where at least a group of k shares out of n shares reveals the secret information, less of it will reveal no information. In our paper we have proposed a new k-n secret sharing scheme for color image where encryption (Division) of the image is done using Random Number generator.
Minimizing Additive Distortion in Steganography Using Syndrome-Trellis Codes
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION FORENSICS & SECURITY
Abstract—This paper proposes a complete practical methodology for minimizing additive distortion in Steganography with general (no binary) embedding operation. Let every possible value of every stego element be assigned a scalar expressing the distortion of an embedding change done by replacing the cover element by this value. The total distortion is assumed to be a sum of per-element distortions. Both the payload-limited sender (minimizing the total distortion while embedding a fixed payload) and the distortion-limited sender (maximizing the payload while introducing a fixed total distortion) are considered. Without any loss of performance, the no binary case is decomposed into several binary cases by replacing individual bits in cover elements. The binary case is approached using a novel syndrome-coding scheme based on dual convolution codes equipped with the Viterbi algorithm. This fast and very versatile solution achieves state-of-the-art results in Steganography applications while having linear time and space complexity w.r.t. the number of cover elements. We report extensive experimental results for a large set of relative payloads and for different distortion profiles, including the wet paper channel. Practical merit of this approach is validated by constructing and testing adaptive embedding schemes for digital images in raster and transform domains. Most current coding schemes used in Steganography (matrix embedding, wet paper codes, etc.) and many new ones can be implemented using this framework.
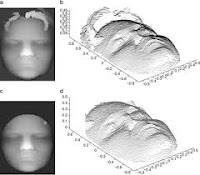
3D Facial Land marking under Expression, Pose, and Occlusion Variations
IEEE 2014 TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMETRICS THEORY, APPLICATIONS AND SYSTEMS
Abstract—Automatic localization of 3D facial features is important for face recognition, tracking, modeling and expression analysis. Methods developed for 2D images were shown to have problems working across databases acquired with different illumination conditions. Expression variations, pose variations and occlusions also hamper accurate detection of landmarks. In this paper we assess a fully automatic 3D facial land marking algorithm that relies on accurate statistical modeling of facial features. This algorithm can be employed to model any facial landmark, provided that the facial poses present in the training and test conditions are similar. We test this algorithm on the recently acquired Bosporus 3D face database, and also inspect cross-database performance by using the FRGC database. Then, a curvature-based method for localizing the nose tip is introduced and shown to perform well under severe conditions
Novel Approach for Color Extended Visual Cryptography Using Error Diffusion
IEEE 2013 TRANSACTIONS ON COMPUTER & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Abstract - Visual cryptography, an emerging cryptography technology, uses the characteristics of human vision to decrypt encrypted images. Cryptography is the study of mathematical techniques related aspects of Information Security such as confidentiality, data security, entity authentication and data origin authentication, but it is not the only means of providing information security, rather one of the techniques. Visual cryptography is a new technique which provides information security which uses simple algorithm unlike the complex, computationally intensive algorithms used in other techniques like traditional cryptography. Previous methods in the literature show good results for black and white or gray scale VC schemes, however, they are not sufficient to be applied directly to color shares due to different color structures. Some methods for color visual cryptography are not satisfactory in terms of producing either meaningless shares or meaningful shares with low visual quality, leading to suspicion of encryption. Color visual cryptography (VC) encrypts a color secret message into color halftone image shares. This project introduces the concept of visual information pixel (VIP) synchronization and error diffusion to attain a color visual cryptography encryption method that produces meaningful color shares with high visual quality. VIP synchronization retains the positions of pixels carrying visual information of Original images throughout the color channels and error diffusion generates shares pleasant to human eyes. Comparisons with previous approaches show the superior performance of the new method.
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering
Abstract—Feature selection involves identifying a subset of the most useful features that produces compatible results as the original entire set of features. A feature selection algorithm may be evaluated from both the efficiency and effectiveness points of view. While the efficiency concerns the time required to find a subset of features, the effectiveness is related to the quality of the subset of features. Based on these criteria, a fast clustering-based feature selection algorithm, FAST, is proposed and experimentally evaluated in this paper. The FAST algorithm works in two steps. In the first step, features are divided into clusters by using graph-theoretic clustering methods. In the second step, the most representative feature that is strongly related to target classes is selected from each cluster to form a subset of features. Features in different clusters are relatively independent, the clustering-based strategy of FAST has a high probability of producing a subset of useful and independent features. To ensure the efficiency of FAST, we adopt the efficient minimum-spanning tree clustering method. The efficiency and effectiveness of the FAST algorithm are evaluated through an empirical study. Extensive experiments are carried out to compare FAST and several representative feature selection algorithms, namely, FCBF, ReliefF, CFS, Consist, and FOCUS-SF, with respect to four types of well-known classifiers, namely, the probability-based Naive Bayes, the tree-based C4.5, the instance-based IB1, and the rule-based RIPPER before and after feature selection. The results, on 35 publicly available real-world high dimensional image, microarray, and text data, demonstrate that FAST not only produces smaller subsets of features but also improves the performances of the four types of classifiers
IEEE 2013: Property Analysis of XOR Based Visual Cryptography
Abstract—A (k, n) Visual Cryptographic Scheme (VCS) encodes a secret image into n shadow images (printed on Transparencies) distributed among n participants. When any k participants superimpose their transparencies on an overhead projector (OR operation), the secret image can be visually revealed by human visual system without computation. However, the monotone property of OR operation degrades the visual quality of reconstructed image for OR-based VCS (OVCS). Accordingly, XOR-based VCS (XVCS), which uses XOR operation for decoding, was proposed to enhance the contrast. In this paper, we investigate the relation between OVCS and XVCS. Our main contribution is to theoretically prove that the basis matrices of (k, n)-OVCS can be used in (k, n)-XVCS. Meantime, the contrast is enhanced 2
(k1) times
IEEE 2013: Securing Visual Cryptographic Shares using Public Key Encryption
Abstract—The Visual Cryptography Scheme is a secure method that encrypts a secret document or image by breaking it into shares. A distinctive property of Visual Cryptography Scheme is that one can visually decode the secret image by superimposing shares without computation. By taking the advantage of this property, third person can easily retrieve the secret image if shares are passing in sequence over the network. The project presents an approach for encrypting visual cryptographically generated image shares using Public Key Encryption. RSA algorithm is used for providing the double security of secret document. Thus secret share are not available in their actual form for any alteration by the adversaries who try to create fake shares. The scheme provides more secure secret shares that are robust against a number of attacks & the system provides a strong security for the handwritten text, images and printed documents over the public network.
IEEE 2013: Super-Resolution-based In painting
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Image Processing
Abstract—This paper introduces a new exemplar-based in painting frame-work. A coarse version of the input image is first in painted by a non-parametric patch sampling. Compared to existing approaches, some improvements have been done (e.g. filling order computation, combination of K nearest neighbor). The in painted of a coarse version of the input image allows to reduce the computational complexity, to be less sensitive to noise and to work with the dominant orientations of image structures. From the low-resolution in painted image, a single-image super-resolution is applied to recover the details of missing areas. Experimental results on natural images and texture synthesis demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method
IEEE 2013: Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted Images by Reserving Room Before Encryption
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
Abstract—Recently, more and more attention is paid to reversible data hiding (RDH) in encrypted images, since it maintains the excellent property that the original cover can be losslessly recovered after embedded data is extracted while protecting the image content’s confidentiality. All previous methods embed data by reversibly vacating room from the encrypted images, which may be subject to some errors on data extraction and/or image restoration. In this paper, we propose a novel method by reserving room before encryption with a traditional RDH algorithm, and thus it is easy for the data hider to reversibly embed data in the encrypted image. The proposed method can achieve real reversibility, that is, data extraction and image recovery are free of any error. Experiments show that this novel method can embed more than 10 times as large payloads for the same image quality as the previous methods, such as for PSNR dB
IEEE 2013: EMR: A Scalable Graph-based Ranking Model for Content-based Image Retrieval
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering
Abstract—Graph-based ranking models have been widely applied in information retrieval area. In this paper, we focus on a well known graph-based model - the Ranking on Data Mani fold model, or Manifold Ranking (MR). Particularly, it has been successfully applied to content-based image retrieval, because of its outstanding ability to discover underlying geometrical structure of the given image database. However, manifold ranking is computationally very expensive, which significantly limits its applicability to large databases especially for the cases that the queries are out of the database (new samples). We propose a novel scalable graph-based ranking model called Efficient Manifold Ranking (EMR), trying to address the shortcomings of MR from two main perspectives: scalable graph construction and efficient ranking computation. Specifically, we build an anchor graph on the database instead of a traditional k-nearest neighbor graph, and design a new form of adjacency matrix utilized to speed up the ranking. An approximate method is adopted for efficient out-of-sample retrieval. Experimental results on some large scale image databases demonstrate that EMR is a promising method for real world retrieval applications.
IEEE 2013: Steganography using Genetic Algorithm along with Visual Cryptography for Wireless Network Application
Abstract—Image Stenography is an emerging field of research for secure data hiding and transmission over networks. The proposed system provides the best approach for Least Significant Bit (LSB) based Stenography using Genetic Algorithm (GA) along with Visual Cryptography (VC). Original message is converted into cipher text by using secret key and then hidden into the LSB of original image. Genetic Algorithm and Visual Cryptography has been used for enhancing the security. Genetic Algorithm is used to modify the pixel location of stego image and the detection of this message is complex. Visual Cryptography is used to encrypt the visual information. It is achieved by breaking the image into two shares based on a threshold. The performance of the proposed system is experimented by performing steganalysis and conducting benchmarking test for analysing the parameters like Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR). The main aim of this paper is to design the enhanced secure algorithm which uses both steganography using Genetic Algorithm and Visual Cryptography to ensure improved security and reliability.
IEEE 2013: Scalable Face Image Retrieval using Attribute-Enhanced Sparse Code words
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Multimedia
Abstract—Photos with people (e.g., family, friends, celebrities, etc.) are the major interest of users. Thus, with the exponentially growing photos, large-scale content-based face image retrieval is an enabling technology for many emerging applications. In this work, we aim to utilize automatically detected human attributes that contain semantic cues of the face photos to improve content-based face retrieval by constructing semantic code words for efficient large-scale face retrieval. By leveraging human attributes in a scalable and systematic framework, we propose two orthogonal methods named attribute-enhanced sparse coding and attribute-embedded inverted indexing to improve the face retrieval in the offline and online stages. We investigate the effectiveness of different attributes and vital factors essential for face retrieval. Experimenting on two public data sets, the results show that the proposed methods can achieve up to 43.5% relative improvement in MAP compared to the existing method
IEEE 2013: AN EXTENDED VISUAL CRYPTOGRAPHY SCHEME WITHOUT PIXEL EXPANSION FOR HALFTONE IMAGES
Abstract—Visual cryptography is a secret sharing scheme which uses images distributed as shares such that, when the shares are superimposed, a hidden secret image is revealed. In extended visual cryptography, the share images are constructed to contain meaningful cover images, thereby providing opportunities for integrating visual cryptography and biometric security techniques. In this paper, we propose a method for processing halftone images that improves the quality of the share images and the recovered secret image in an extended visual cryptography scheme for which the size of the share images and there covered image is the same as for the original halftone secret image. The resulting scheme maintains the perfect security of the original extended visual cryptography approach
IEEE 2013: An Encryption and Decryption Algorithm for Image Based on DNA
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Communication Systems and Network Technologies
Abstract—A novel image encryption algorithm based on DNA sequence addition operation. This initiation and increasing escalation of Internet has caused the information to be paperless and the makeover into electronic compared to the conventional digital image distribution. In this paper we proposed and implement four phase. First phase, image is renovating into binary matrix. Afterward matrix is apportioning into equal blocks. Second phase, each block is then encoded into DNA sequences and DNA sequence addition operation used to add these blocks. For that result of added matrix is achieved by using two Logistic maps. At the time of decoding the DNA sequence matrix is complemented and we encrypt that result by using DES then we get encrypted image. Our paper includes a novel encryption technique for providing security to image. We have proposed an algorithm which is based on suitable encryption method
IEEE 2013: Combined texture and Shape Features for Content Based Image Retrieval
IEEE 2013 Transactions on Power and Computing Technologies
Abstract—Image retrieval refers to extracting desired images from a large database. The retrieval may be of text based or content based. Here content based image retrieval (CBIR) is performed. CBIR is a long standing research topic in the field of multimedia. Here features such as texture & shape are analyzed. Gabor filter is used to extract texture features from images. Morphological c10sing operation combined with Gabor filter gives better retrieval accuracy. The parameters considered are scale and orientation. After applying Gabor filter on the image, texture features such as mean and standard deviations are calculated. This forms the feature vector. Shape feature is extracted by using Fourier Descriptor and the centroid distance. In order to improve the retrieval performance, combined texture and shape features are utilized, because many features provide more information than the single feature. The images are extracted based on their Euclidean distance. The performance is evaluated using precision-recall graph.
IEEE 2013: Beyond Text QA: Multimedia Answer Generation by Harvesting Web Information
IEEE 2013 Transactions on multimedia
Abstract—Community question answering (cQA) services have gained popularity over the past years. It not only allows community members to post and answer questions but also enables general users to seek information from a comprehensive set of well-answered questions. However, existing cQA forums usually provide only textual answers, which are not informative enough for many questions. In this paper, we propose a scheme that is able to en-rich textual answers in cQA with appropriate media data. Our scheme consists of three components: answer medium selection, query generation for multimedia search, and multimedia data selection and presentation. This approach automatically determines which type of media information should be added for a textual answer. It then automatically collects data from the web to enrich the answer. By processing a large set of QA pairs and adding them to a pool, our approach can enable a novel multimedia question answering (MMQA) approach as users can find multimedia answers by matching their questions with those in the pool. Different from a lot of MMQA research efforts that attempt to directly answer questions with image and video data, our approach is built based on community-contributed textual answers and thus it is able to deal
with more complex questions. We have conducted extensive experiments on a multi source QA data set. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach
with more complex questions. We have conducted extensive experiments on a multi source QA data set. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach
IEEE 2012 TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING
Abstract— With many potential practical applications, content- based image retrieval (CBIR) has attracted substantial attention during the past few years. A variety of relevance feedback (RF) schemes have been developed as a powerful tool to bridge the semantic gap between low-level visual features and high-level semantic concepts, and thus to improve the performance of CBIR systems. Among various RF approaches, support-vector-machine (SVM)-based RF is one of the most popular techniques in CBIR. Despite the success, directly using SVM as an RF scheme has two main drawbacks. First, it treats the positive and negative feedbacks equally, which is not appropriate since the two groups of training feedbacks have distinct properties. Second, most of the SVM- based RF techniques do not take into account the unlabeled samples, although they are very helpful in constructing a good classifier. To explore solutions to overcome these two drawbacks, in this paper, we propose a biased maximum margin analysis (BMMA) and a semi supervised BMMA (Semi BMMA) for integrating the distinct properties of feed backs and utilizing the information of unlabeled samples for SVM-based RF schemes. The BMMA differentiates positive feed backs from negative ones based on local analysis, whereas the Semi BMMA can effectively integrate information of unlabeled samples by introducing a Laplacian regularizer to the BMMA. We formally formulate this problem into a general subspace learning task and then propose an automatic approach of determining the dimensionality of the embedded subspace for RF. Extensive experiments on a large real-world image database demonstrate that the proposed scheme combined with the SVM RF can significantly improve the performance of CBIR systems.
IEEE 2012: Learn to Personalized Image Search from the Photo Sharing Websites
IEEE 2012 TRANSACTIONS ON MULTIMEDIA
Abstract— Increasingly developed social sharing websites, like Flicker and YouTube, allow users to create, share, annotate and comment medias. The large-scale user-generated meta-data not only facilitate users in sharing and organizing multimedia content, but provide useful information to improve media retrieval and management. Personalized search serves as one of such examples where the web search experience is improved by generating the returned list according to the modified user search intents. In this paper, we exploit the social annotations and propose a novel framework simultaneously considering the user and query relevance to learn to personalized image search. The basic premise is to embed the user preference and query-related search intent into user-specific topic spaces. Since the users’ original annotation is too sparse for topic modeling, we need to enrich users’ annotation pool before user-specific topic spaces construction. The proposed framework contains two components: 1) A Ranking based Multi-correlation Tensor Factorization model is proposed to perform annotation prediction, which is considered as users’ potential annotations for the images; 2) We introduce
User-specific Topic Modeling to map the query relevance and user preference into the same user-specific topic space. For performance evaluation, two resources involved with users’ social Activities are employed. Experiments on a large-scale Flicker dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
IEEE 2012: Face Recognition using Sparse Approximated Nearest Points between Image Sets
IEEE TRANSACTION ON PATTERN ANALYSIS AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
Abstract— We propose an efficient and robust solution for image set classification. A joint representation of an image set is proposed which includes the image samples of the set and their affine hull model. The model accounts for unseen appearances in the form of affine combinations of sample images. To calculate the between-set distance, we introduce the Sparse Approximated Nearest Point (SANP). SANPs are the nearest points of two image sets such that each point can be sparsely approximated by the image samples of its respective set. This novel sparse formulation enforces sparsity on the sample coefficients and jointly optimizes the nearest points as well as their sparse approximations. Unlike standard sparse coding, the data to be sparsely approximated is not fixed. A convex formulation is proposed to find the optimal SANPs between two sets and the accelerated proximal gradient method is adapted to efficiently solve this optimization. We also derive the kernel extension of the SANP and propose an algorithm for dynamically tuning the RBF kernel parameter while matching each pair of image sets. Comprehensive experiments on the UCSD/Honda, CMU MoBo and YouTube Celebrities face datasets show that our method consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art.
IEEE 2012 : Separable Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted Image
IEEE 2012 TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION FORENSICS AND SECURITY
Abstract— This work proposes a novel scheme for separable reversible data hiding in encrypted images. In the first phase, a content owner encrypts the original uncompressed image using an encryption key. Then, a data-hider may compress the least significant bits of the encrypted image using a data-hiding key to create a sparse space to accommodate some additional data. With an encrypted image containing additional data, if a receiver has the data-hiding key, he can extract the additional data though he does not know the image content. If the receiver has the encryption key, he can decrypt the received data to obtain an image similar to the original one, but cannot extract the additional data. If the receiver has both the data-hiding key and the encryption key, he can extract the additional data and recover the original content without any error by exploiting the spatial correlation in natural image when the amount of additional data is not too large.
IEEE 2012, 11-13 April 2012, Vienna, Austria
Abstract—The paper presents a robust and secure Multi-modal strategy for watermarking of the digital images. In this approach, the image is divided into blocks. The blocks are first permuted according to a pseudo random key. All the blocks of the original image are statistically analyzed and the watermarks embedded into only those blocks in which the standard deviation of the image pixel intensities is greater than predefined threshold. Leaving some of the blocks underwater marked decreases chances of blind detection by the attacker due to probability of false detection from the non water marked blocks. The watermark is embedded in the blocks using randomly selected transformation strategies using any of the three transforms, viz. Discrete Cosine Transform, Discrete Fourier Transform, and Discrete Wavelet Transform. Each block is independently watermarked with one unique share of original watermark generated through threshold visual cryptography method. Encrypting the watermark before embedding makes the watermark detection and removal very difficult making insecure. Experimental results depict the robustness of the algorithm against prevalent image processing attacks like rotation, scaling, compression, noise addition and filtering,etc..
IEEE 2012 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTING, ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGIES
Abstract— Core banking is a set of services provided by a group of networked bank branches. Bank customers may access their funds and perform other simple transactions from any of the member branch offices. The major issue in core banking is the authenticity of the customer. Due to unavoidable hacking of the databases on the internet, it is always quite difficult to trust the information on the internet. To solve this problem of authentication, we are proposing an algorithm based on image processing, improved Steganography and visual cryptography. This paper proposes technique of encode the password of a customer by improved Steganography, most of the Steganography techniques use either three or four adjacent pixels around a target pixel whereas the proposed technique is able to utilize at most all eight adjacent neighbors so that imperceptibility value grows bigger. and then dividing it into shares. Total number of shares to be created is depending on the scheme chosen by the bank. When two shares are created, one is stored in the Bank database and the others kept by the customer. The customer has to present the share during all of his transactions. This share is stacked with the first share to get the original image. Then decoding method issued to take the hidden password on acceptance or rejection of the output and authenticate the customer
IEEE 2012 POWER,SIGNALS,CONTROLS ANDCOMPUTATION(EPSCICON),
Abstract— With the advent of internet, various online attacks has been increased and among them the most popular attack is phishing. Phishing is an attempt by an individual or a group to get personal confidential information such as passwords, credit card information from unsuspecting victims for identity theft, financial gain and other fraudulent activities. Fake websites which appear very similar to the original ones are being hosted to achieve this. In this paper we have proposed a new approach named as "A Novel Anti-phishing framework based on visual cryptography "to solve the problem of phishing. Here an image based authentication using Visual Cryptography is implemented. The use of visual cryptography is explored to preserve the privacy of an image captcha by decomposing the original image captcha into two shares (known as sheets) that are stored in separate database servers(one with user and one with server) such that the original image captcha can be revealed only when both are simultaneously available; the individual sheet images do not reveal the identity of the original image captcha. Once the original image captcha is revealed to the user it can be used as the password. Using this website cross verifies its identity and proves that it is a genuine website before the end users.
IEEE 2012 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
Abstract— Maintaining the secrecy and confidentiality of images is a vibrant area of research, with two different approaches being followed, the first being encrypting the images through encryption algorithms using keys, the other approach involves dividing the image into random shares to maintain the images secrecy. Unfortunately heavy computation cost and key management limit the employment of the first approach and the poor quality of the recovered image from the random shares limit the applications of the second approach. In this paper we propose a novel approach without the use of encryption keys. The approach employs Sieving, Division and Shuffling to generate random shares such that with minimal computation, the original secret image can be recovered from the random shares without any loss of image quality.
2012 IEEE STUDENTS’ CONFERENCE ON ELECTRICAL, ELECTRONICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
Abstract— Visual Cryptography is the study of mathematical techniques related aspects of Security which allows Visual information to be encrypted in such a way that their decryption can be performed by the human visual system, without any complex cryptographic algorithms. Visual cryptography scheme is used to encrypt an image into multiple shares and is distributed among different participants. A minimum number of shares if overlapped could reveal the hidden information visually. In a computer a logical OR operation could reveal the sameInformation We propose the significance in use of hybrid half toning in visual cryptography. We also propose a new technique in hiding the information that the encrypted shares are encrypted by inter pixel exchanging using a secondary image.
IEEE SIGNAL PROCESSING LETTERS, APRIL 2012
Abstract—This letter proposes an improved version of Zhang’s reversible data hiding method in encrypted images. The original work partitions an encrypted image into blocks, and each block carries one bit by flipping three LSBs of a set of pre-defined pixels. The data extraction and image recovery can be achieved by examining the block smoothness. Zhang’s work did not fully exploit the pixels in calculating the smoothness of each block and did not consider the pixel correlations in the border of neighboring blocks. These two issues could reduce the correctness of data extraction. This letter adopts a better scheme for measuring the smoothness of blocks, and uses the side-match scheme to further decrease the error rate of extracted-bits. The experimental results reveal that the proposed method offers better performance over Zhang’s work. For example, when the block size is set to 8 8, the error rate of the Lena image of the proposed method is 0. 34%, this is significantly lower than 1.21% of Zhang’s work
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, OCTOBER 2011
Abstract—Digital image libraries and other multimedia databases have been dramatically expanded in recent years. In order to effectively and precisely retrieve the desired images from a large image database, the development of a content-based image retrieval (CBIR) system has become an important research issue. However, most of the proposed approaches emphasize on finding the best representation for different image features. Furthermore, very few of the representative works well consider the user’s subjectivity and preferences in the retrieval process. In this paper, a user-oriented mechanism for CBIR method based on an interactive genetic algorithm (IGA) is proposed. Color attributes like the mean value, the standard deviation, and the image bitmap of a color image are used as the features for retrieval. In addition, the entropy based on the gray level co-occurrence matrix and the edge histogram of an image is also considered as the texture features. Furthermore, to reduce the gap between the retrieval results and the users’ expectation, the IGA is employed to help the users identify the images that are most satisfied to the users’ need. Experimental results and comparisons demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION FORENSICS AND SECURITY, JUNE 2011
Abstract— A visual cryptography scheme (VCS) is a kind of secret sharing scheme which allows the encoding of a secret image into shares distributed to participants. The beauty of such a scheme is that a set of qualified participants is able to recover the secret image without any cryptographic knowledge and computation devices. An extended visual cryptography scheme (EVCS) is a kind of VCS which consists of meaningful shares (compared to the random shares of traditional VCS). In this paper, we propose a construction of EVCS which is realized by embedding random shares into meaningful covering shares, and we call it the embedded EVCS. Experimental results compare some of the well-known EVCSs proposed in recent years systematically, and show that the proposed embedded EVCS has competitive visual quality compared with many of the well-known EVCSs in the literature. In addition, it has many specific advantages against these well-known EVCSs, respectively.
Abstract— Visual Cryptography is a special encryption technique to hide information in images in such a way that it can be decrypted by the human visual system. The benefit of the visual secret sharing scheme is in its decryption process where without any complex cryptographic computation encrypted data is decrypted using Human Visual System (HVS). But the encryption technique needs cryptographic computation to divide the image into a number of parts let n. k-n secret sharing scheme is a special type of Visual Cryptographic technique where at least a group of k shares out of n shares reveals the secret information, less of it will reveal no information. In our paper we have proposed a new k-n secret sharing scheme for color image where encryption (Division) of the image is done using Random Number generator.
Embedded security algorithm (CISEA)
IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPUTER & COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY -2011
Abstract— Visual Cryptography is an encryption technique used to hide visual information in such a way that it can be decrypted by the human visual system, without using any decryption algorithm. There exist various schemes like digital watermarking algorithm etc. In this paper we have proposed a new algorithm to enhance the security in visual cryptography. To achieve this level of security, we have proposed a Cover Image Share Embedded security algorithm (CISEA) to produce the meaningful shares from the secret image. In this algorithm we have applied a new concept for generation of compliment images of a cover image over which the shares of secret image are to be embedded. CISEA provides one more layer of security for the images in communication channel. It is shown that CISEA provides better security compared to security provided by visual cryptography using digital watermarking system and the results are tested using MS visual studio dot net platform.
IEEE INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON APPLIED MACHINE INTELLIGENCE AND INFORMATICS • JANUARY, 2011
Abstract— The content based image retrieval (CBIR) is one of the most popular, rising research areas of the digital image processing. Most of the available image search tools, such as Google Images and Yahoo! Image search, are based on textual annotation of images. In these tools, images are manually annotated with keywords and then retrieved using text-based search methods. The performances of these systems are not satisfactory. The goal of CBIR is to extract visual content of an image automatically, like color, texture, or shape. This paper aims to introduce the problems and challenges concerned with the design and the creation of CBIR systems, which is based on a free hand sketch (Sketch based image retrieval – SBIR). With the help of the existing methods, describe a possible solution how to design and implement a task spesi_c descriptor, which can handle the informational gap between a sketch and a colored image, making an opportunity for the efficient search hereby. The used descriptor is constructed after such special sequence of preprocessing steps that the transformed full color image and the sketch can be compared. We have studied EHD, HOG and SIFT. Experimental results on two sample databases showed good results. Overall, the results show that the sketch based system allows users an intuitive access to search-tools. The SBIR technology can be used in several applications such as digital libraries, crime prevention, and photo sharing sites. Such system has great value in apprehending suspects and indentifying victims in forensics and law enforcement. A possible application is matching a forensic sketch to a gallery of mug shot images. The area of retrieve images based on the visual content of the query picture intensi_ed recently, which demands on the quite wide methodology spectrum on the area of the image processing
IEEE 2011 TRANSACTION ON COMMUNICATIONS AND SIGNAL PROCESSING
Abstract— Security has become an inseparable issue even in the field of space technology. Visual Cryptography is the study of mathematical techniques related aspects of Information Security which allows Visual information to be encrypted in such a way that their decryption can be performed by the human visual system, without any complex cryptographic algorithms. This technique represents the secret image by several different shares of binary images. It is hard to perceive any clues about a secret image from individual shares. The secret message is revealed when parts or all of these shares are aligned and stacked together. In this paper we provide an overview of the emerging Visual Cryptography (VC) techniques used in the secure transfer of the thousands of images collected by the satellite which are stored in image li brary and sent to Google for use on Google Earth and Google maps. The related work is based on the recovering of secret image using a binary logo which is used to represent the ownership of the host image which generates shadows by visual cryptography algorithms. An error correction coding scheme is also nosed to create the appropriate shadow. The logo extracted from the half-toned host image identifies the cheating types. Furthermore, the logo recovers the reconstructed image when shadow is being cheated nosing an image self verification scheme based on the Rehash technique which rehash the halftone logo for effective self verification of the reconstructed secret image without the need for the trusted third party(TTP).







































No comments:
Post a Comment